Peer-to-Peer Lending Loans: How It Works introduces readers to the fascinating world of peer-to-peer lending, shedding light on its inner workings and benefits in a clear and engaging manner.
Exploring the application process, risk factors, and regulatory aspects, this overview sets the stage for a comprehensive understanding of peer-to-peer lending.
Introduction to Peer-to-Peer Lending Loans
Peer-to-peer lending, also known as P2P lending, is a method of debt financing that enables individuals to borrow and lend money without the involvement of a traditional financial institution like a bank. In this type of lending, borrowers are connected directly with investors through online platforms, cutting out the middleman.
How Peer-to-Peer Lending Differs from Traditional Lending
Peer-to-peer lending differs from traditional lending in several ways. Unlike banks, P2P platforms match borrowers with individual investors willing to lend money, creating a more personalized and often quicker loan approval process. Additionally, P2P lending typically offers lower interest rates for borrowers and potentially higher returns for investors compared to traditional financial institutions.
Benefits of Peer-to-Peer Lending for Borrowers and Investors
- Borrowers can often secure loans at lower interest rates than those offered by banks.
- Investors have the opportunity to earn higher returns compared to traditional savings accounts or investments.
- P2P lending platforms provide a more streamlined and efficient borrowing and lending process.
- Both borrowers and investors can benefit from the direct connection and transparency offered by P2P lending.
Key Players Involved in Peer-to-Peer Lending Platforms
- Borrowers: Individuals looking to secure loans for various purposes, such as debt consolidation, home improvement, or small business funding.
- Investors: Individuals or institutions willing to lend money to borrowers in exchange for interest payments.
- P2P Platforms: Online platforms that facilitate the connection between borrowers and investors, handling loan origination, servicing, and collection processes.
- Credit Scoring Agencies: Entities that assess the creditworthiness of borrowers to determine their risk profile for potential lenders.
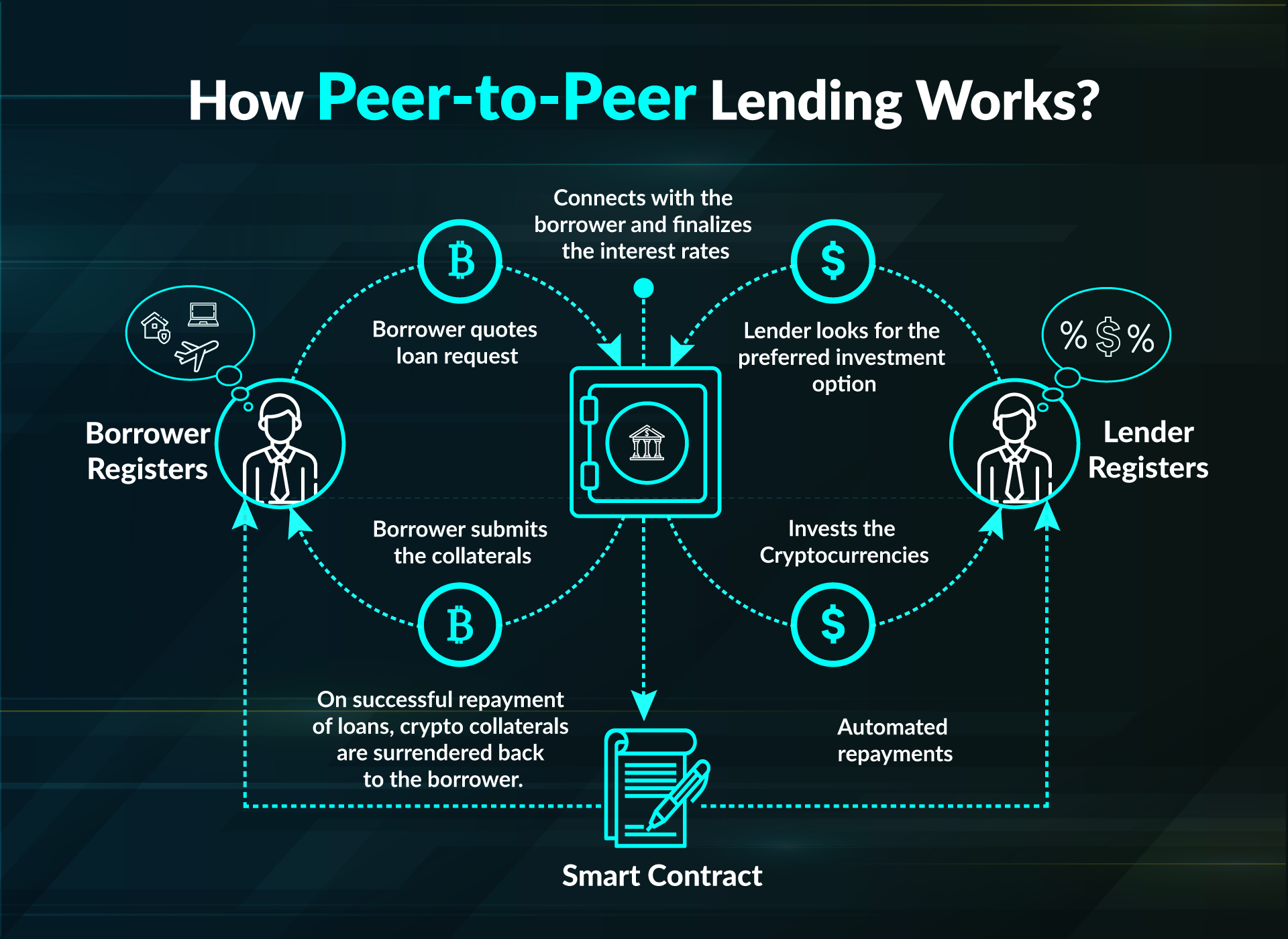
How Peer-to-Peer Lending Works
Peer-to-peer lending, also known as P2P lending, is a method of debt financing that enables individuals to borrow and lend money without the use of an official financial institution as an intermediary. Here’s how the process typically works:
Applying for a Loan on a Peer-to-Peer Lending Platform
When applying for a loan on a peer-to-peer lending platform, borrowers start by creating an account and providing personal and financial information. This information helps the platform assess the borrower’s creditworthiness and assign an appropriate interest rate to the loan.
Borrowers Matched with Potential Lenders
Once the borrower’s information is verified and approved, the peer-to-peer lending platform matches the borrower with potential lenders who are willing to fund the loan. Lenders can choose to fund a portion or the full amount of the loan, spreading their investment across multiple borrowers to reduce risk.
Role of Interest Rates in Peer-to-Peer Lending
Interest rates in peer-to-peer lending are determined based on the borrower’s credit profile, loan amount, and term length. Generally, borrowers with higher credit scores are offered lower interest rates, while riskier borrowers may face higher rates to compensate lenders for the increased risk.
Popular Peer-to-Peer Lending Platforms
Some popular peer-to-peer lending platforms include LendingClub, Prosper, Upstart, and Funding Circle. These platforms provide a marketplace where borrowers can access funding from individual investors, offering competitive rates and flexible loan terms.
Risk Factors in Peer-to-Peer Lending
Peer-to-peer lending, like any other investment or loan option, comes with its own set of risks that both borrowers and lenders should be aware of. Understanding these risks is crucial in making informed decisions and managing expectations when participating in peer-to-peer lending platforms.
Risks Associated with Peer-to-Peer Lending
- Default Risk: One of the primary risks in peer-to-peer lending is the potential for borrowers to default on their loans, leading to loss of principal for lenders.
- Platform Risk: The platform itself may face financial instability, regulatory issues, or even fraudulent activities, impacting the funds invested by lenders.
- Illiquidity Risk: Unlike traditional bank loans, peer-to-peer lending investments are not easily liquidated, making it challenging to access funds quickly in case of emergencies.
- Interest Rate Risk: Fluctuations in interest rates can affect the returns earned by lenders, especially in fixed-rate loans where the interest rate is locked in.
Comparison with Traditional Bank Loans
- Less Regulation: Peer-to-peer lending platforms are often less regulated compared to traditional banks, increasing the risk of fraud and misconduct.
- Higher Default Rates: Due to the nature of peer-to-peer lending catering to borrowers with lower credit scores, the risk of default is generally higher than with traditional bank loans.
- Diversification Opportunities: While traditional banks offer standardized loan products, peer-to-peer lending allows for diversification of investments across different borrower profiles and risk levels.
Strategies to Mitigate Risks
- Due Diligence: Both borrowers and lenders should conduct thorough research on the platforms, borrowers, and loan terms before committing to any peer-to-peer lending transactions.
- Diversification: Lenders can mitigate risk by spreading their investments across multiple loans to reduce exposure to any single borrower defaulting.
- Risk Assessment Tools: Utilizing risk assessment tools provided by the platforms can help lenders evaluate the creditworthiness of borrowers and make informed investment decisions.
Regulation and Legality
Peer-to-peer lending platforms operate within a regulatory framework that aims to protect both lenders and borrowers. Understanding the legal requirements for operating in this space is crucial to ensure compliance and maintain trust within the industry.
Regulatory Environment
Peer-to-peer lending is regulated by financial authorities in many countries to safeguard investor interests and ensure fair practices. Regulations may vary depending on the region, but common aspects include licensing, disclosure requirements, and risk management guidelines.
- Platforms may need to obtain specific licenses to operate legally, ensuring they meet certain financial stability and operational standards.
- Regulators often mandate platforms to provide transparent information to investors, including details on loan terms, risks, and fees.
- Guidelines on risk management help platforms assess borrower creditworthiness, manage loan defaults, and protect investor funds.
Legal Requirements
Operating a peer-to-peer lending platform involves navigating a complex legal landscape to comply with consumer protection laws, data privacy regulations, and anti-money laundering measures. Platforms must adhere to these requirements to safeguard user data and prevent fraudulent activities.
- Platforms are typically required to implement robust data security measures to protect sensitive borrower and investor information.
- Compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) regulations involves verifying user identities, monitoring transactions for suspicious activities, and reporting any irregularities to authorities.
- Adherence to consumer protection laws ensures that borrowers are treated fairly, with clear terms and conditions outlined in loan agreements.
Recent Developments
In recent years, peer-to-peer lending regulations have evolved to address emerging challenges and opportunities in the fintech sector. Regulators have introduced new guidelines to promote innovation while safeguarding against potential risks, fostering a more robust ecosystem for peer-to-peer lending.
- Regulatory authorities have focused on enhancing transparency and accountability in the industry, encouraging platforms to disclose more information to investors.
- Changes in regulations aim to promote responsible lending practices, mitigate risks of loan defaults, and improve overall market integrity.
- Regulators are working closely with industry stakeholders to ensure that peer-to-peer lending continues to thrive in a regulated environment, balancing innovation with investor protection.
Peer-to-Peer Lending vs. Traditional Banking
Peer-to-peer lending and traditional banking are two distinct ways of borrowing and lending money, each with its own set of benefits and drawbacks. Let’s explore how they differ and what impact peer-to-peer lending has on the banking industry.
Benefits of Peer-to-Peer Lending Compared to Traditional Banking
- Accessibility: Peer-to-peer lending platforms often provide easier access to loans for individuals who may not qualify for traditional bank loans due to strict eligibility criteria.
- Competitive Interest Rates: Peer-to-peer lending platforms can offer more competitive interest rates compared to traditional banks, providing borrowers with potentially lower costs for borrowing.
- Diverse Investment Opportunities: Peer-to-peer lending allows individual investors to diversify their portfolios by investing in loans, offering them an alternative investment option beyond traditional stocks and bonds.
Impact of Peer-to-Peer Lending on the Banking Industry
- Competition: Peer-to-peer lending platforms introduce competition into the lending market, forcing traditional banks to innovate and improve their services to remain competitive.
- Disintermediation: Peer-to-peer lending eliminates the need for traditional financial institutions as intermediaries, directly connecting borrowers and investors, potentially reducing costs for both parties.
- Regulatory Challenges: The rise of peer-to-peer lending has challenged traditional regulatory frameworks, leading to a reevaluation of existing laws and regulations governing the financial industry.
Interest Rates Offered by Peer-to-Peer Lending Platforms vs. Traditional Banks
- Peer-to-Peer Lending: Interest rates on peer-to-peer lending platforms are often determined by the platform itself and can vary based on factors such as creditworthiness of the borrower and demand from investors.
- Traditional Banks: Traditional banks typically offer fixed interest rates on loans, based on the bank’s cost of funds and the borrower’s credit risk profile.
- Comparison: While peer-to-peer lending platforms may offer lower interest rates in some cases, traditional banks provide a sense of security and stability due to their long-standing presence in the financial industry.
Peer-to-Peer Lending for Small Businesses
Peer-to-peer lending offers a valuable alternative funding source for small businesses looking to grow or stabilize their operations. By connecting individual investors with small business owners, these platforms facilitate loans that may be more accessible than traditional bank loans.
Benefits for Small Businesses
- Flexible Terms: Small businesses can negotiate terms directly with individual lenders, often leading to more flexible loan terms compared to banks.
- Quick Approval: The streamlined application process and automated underwriting on peer-to-peer platforms can result in faster approval times.
- Lower Interest Rates: Small businesses may secure lower interest rates on peer-to-peer loans, especially if they have a strong credit profile.
Application Process
- Registration: Small businesses need to create an account on the peer-to-peer lending platform and provide details about their business.
- Loan Request: Businesses can then submit a loan request outlining the purpose of the loan, desired amount, and proposed terms.
- Review and Approval: Individual lenders review loan requests and decide whether to fund them based on the business’s creditworthiness and financials.
Success Stories
One example is a small bakery that used peer-to-peer lending to purchase new equipment and expand their product line. With the funds raised, they were able to increase production and reach new customers, leading to a significant revenue boost.
Another success story involves a tech startup that secured a peer-to-peer loan to hire additional developers and launch a new software product. The investment paid off as the new product gained traction in the market, generating substantial revenue for the business.
Peer-to-Peer Lending and Credit Scores
Credit scores play a crucial role in peer-to-peer lending as they are used by platforms to assess the creditworthiness of borrowers. Here’s how credit scores impact loan approval and interest rates and some tips for borrowers to improve their credit scores for peer-to-peer lending.
Role of Credit Scores in Peer-to-Peer Lending
- Credit scores are used by peer-to-peer lending platforms to evaluate the risk associated with lending money to a borrower.
- Higher credit scores generally indicate a lower risk of default, making borrowers more attractive to lenders.
- Borrowers with higher credit scores are likely to qualify for larger loan amounts and lower interest rates.
Impact of Credit Scores on Loan Approval and Interest Rates
- Borrowers with excellent credit scores are more likely to get approved for loans compared to those with poor credit scores.
- Higher credit scores can result in lower interest rates, saving borrowers money over the life of the loan.
- Lenders may offer more favorable loan terms to borrowers with good credit scores, such as longer repayment periods.
Tips to Improve Credit Scores for Peer-to-Peer Lending
- Pay bills on time to establish a positive payment history.
- Reduce credit card balances to lower credit utilization ratios.
- Regularly check credit reports for errors and dispute any inaccuracies.
- Avoid opening multiple new credit accounts in a short period of time.
- Consider using credit-building tools or services to boost credit scores.
Peer-to-Peer Lending and Diversification
Peer-to-peer lending can be a valuable tool for investors looking to diversify their portfolios. By spreading investments across multiple peer-to-peer loans, investors can reduce the impact of any single loan defaulting and minimize overall risk in their investment strategy.
The Benefits of Diversification in Peer-to-Peer Lending
Diversification in peer-to-peer lending involves spreading investments across a range of borrowers with different risk profiles. This strategy helps to reduce the impact of any one borrower defaulting on their loan, as the losses can be offset by the returns from other successful loans. By diversifying, investors can potentially earn a more stable return over time.
- Diversification minimizes the impact of individual loan defaults.
- It helps to spread risk across a variety of borrowers and loan types.
- Investors can achieve a more consistent return by diversifying their peer-to-peer lending investments.
Examples of Diversification Minimizing Risk
For example, if an investor only lends money to one borrower and that borrower defaults, the investor loses the entire investment. However, if the investor spreads their investment across ten different borrowers and one defaults, the impact is significantly reduced. The returns from the other successful loans can help to offset the loss from the defaulting loan, resulting in a more stable overall return for the investor.
Diversification is key to reducing risk in peer-to-peer lending and can help investors achieve a more consistent return over time.
Transparency and Information Sharing
Transparency plays a crucial role in peer-to-peer lending, as it builds trust between borrowers and lenders. By ensuring transparency, both parties can make informed decisions and understand the risks involved in the lending process.
Types of Information Shared
- Loan Details: Peer-to-peer platforms provide detailed information about the loan, including the amount, interest rate, term, and purpose. This helps investors assess the risk and potential return of the investment.
- Borrower Information: Borrower profiles, credit history, and financial background are shared with lenders to help them evaluate the creditworthiness of the borrower.
- Risk Factors: Platforms disclose risk factors associated with each loan, such as default rates, late payment penalties, and collection processes. This transparency helps investors make informed decisions based on their risk tolerance.
- Fees and Charges: All fees and charges associated with the loan, including origination fees, servicing fees, and late payment fees, are clearly outlined to both borrowers and lenders.
Peer-to-Peer Lending and the Economy
Peer-to-peer lending has a significant impact on the economy by providing an alternative source of financing outside of traditional banking systems. This form of lending can stimulate economic growth by connecting borrowers directly with individual investors, cutting out the middleman and reducing costs. However, there are also challenges and concerns related to the role of peer-to-peer lending in the economy that need to be addressed.
Impact on Economic Growth
Peer-to-peer lending can stimulate economic growth by providing access to credit for individuals and small businesses who may have difficulty obtaining loans from traditional financial institutions. This increased access to capital can fuel entrepreneurship, innovation, and overall economic activity. By facilitating the flow of funds between individuals, peer-to-peer lending can contribute to a more efficient allocation of resources in the economy.
Challenges and Concerns
One of the main challenges related to peer-to-peer lending in the economy is the potential for increased risk due to the lack of regulation and oversight compared to traditional banking. There are concerns about the quality of underwriting standards, the potential for fraud, and the impact of economic downturns on the performance of peer-to-peer loans. Additionally, the rapid growth of the peer-to-peer lending industry raises questions about its systemic risk and the potential for market disruptions in the event of a crisis.
Future Trends in Peer-to-Peer Lending
Peer-to-peer lending has been rapidly evolving over the years, and it is crucial to anticipate future trends in this industry to stay ahead of the curve. Technological advancements and innovative solutions are likely to play a significant role in shaping the future of peer-to-peer lending. Let’s explore some potential trends that could impact the way peer-to-peer lending operates in the coming years.
Increased Automation and Artificial Intelligence
With the advancements in technology, we can expect to see a rise in automation and the use of artificial intelligence in the peer-to-peer lending process. This could streamline the loan approval process, enhance risk assessment capabilities, and improve overall efficiency in matching borrowers with investors.
Blockchain and Smart Contracts
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize peer-to-peer lending by providing a secure and transparent platform for transactions. Smart contracts could automate the lending process, eliminate the need for intermediaries, and reduce the risk of fraud or default.
Global Expansion and Cross-Border Lending
As peer-to-peer lending platforms become more established and regulated, we may see an increase in cross-border lending opportunities. This could open up new markets for borrowers and investors, allowing for greater diversification and access to funding on a global scale.
Integration with Traditional Financial Institutions
In the future, we could see more collaboration between peer-to-peer lending platforms and traditional financial institutions. This partnership could lead to hybrid lending models that combine the strengths of both sectors, offering borrowers more options and investors greater diversification opportunities.
Focus on ESG Criteria
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria are becoming increasingly important in the financial industry. Peer-to-peer lending platforms may start incorporating ESG considerations into their lending decisions, attracting socially responsible investors and borrowers who prioritize sustainability and ethical practices.
Regulatory Developments
Regulatory bodies around the world are keeping a close eye on the peer-to-peer lending industry. Future trends may include more stringent regulations to protect investors and borrowers, as well as promote transparency and fair practices in the lending market.
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, Peer-to-Peer Lending Loans: How It Works offers a glimpse into the future trends and impact of this innovative financial model, leaving readers informed and intrigued by its potential.